-
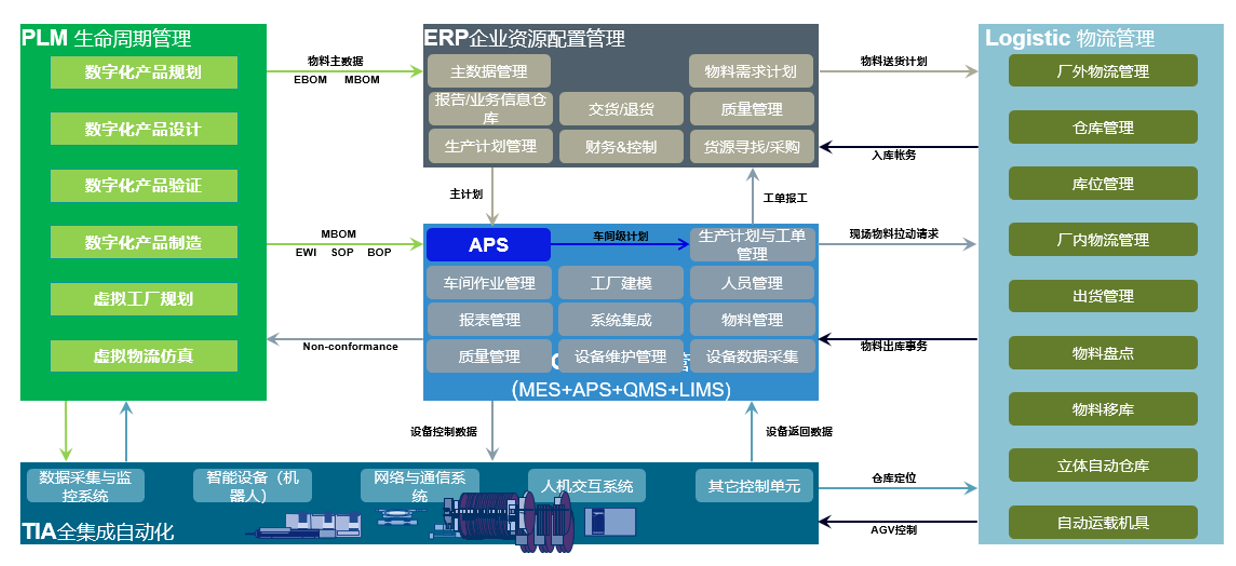
Production plan: Relying on experience, lack of algorithm models, repetitive tasks, limited utilization of constraints, multi-system collaboration, single operation insertion, slow response to anomalies
-
Production Management: Data silos, low effectiveness, manual statistics, high operational requirements, low transparency in the production process, difficult to ensure accuracy, risk of data errors, and inadequate monitoring of process standardization implementation.
-
Quality Management: Insufficient data analysis and reuse, inadequate supervision and guidance of quality tasks, low traceability efficiency, scattered data, inability to obtain inspection information in real time, system deficiencies, and difficulties in actual implementation.
-
Equipment & Energy: Lack of real-time monitoring capabilities, sharing of spare parts information, complete data support for OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness), fault analysis, etc. The PDCA closed-loop management is difficult to implement. The emergency response team cannot effectively reduce energy consumption through data analysis.
-
Material Management: Inability to obtain inventory data in real time, repetitive tasks, low efficiency in passing in-out material information, and inability to meet the material requirements for production plans.
Beverage

Industry pain points
Advantages and Effects of the Plan
Solution
Typical case

